Ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate, acetylcysteine and choline alphoscerate improve mitochondrial function under condition of cerebral ischemia in rat
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3329/bjp.v14i3.40977Keywords:
Acetylcysteine, Cerebral ischemia, Choline alphoscerate, Ethylmethylhydroxypyridine, Mitochondrial function, RatAbstract
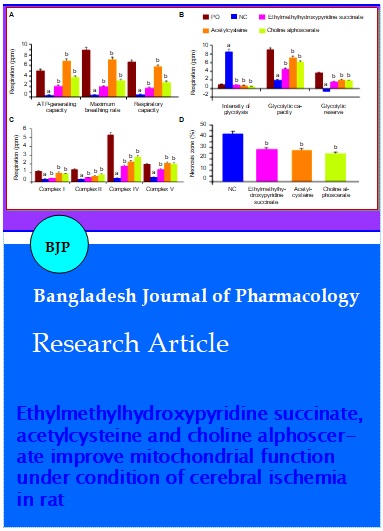
The study was devoted to see the effect of ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate, acetylcysteine and choline alphoscerate on the mitochondrial function under condition of experimental cerebral ischemia in rat. An integrated approach was used with the assessment of changes in the respirometric and antiapoptotic functions of mitochondria. It was found that the application of the objects under study contributed to a decrease in the intensity of glycolysis and the restoration of aerobic glucose metabolism with an increase in ATP synthesis, as well as a decrease in the dissociation of reactions in mitochondrial complexes I, II, IV and V. In addition, the introduction of the studied drugs reduced the intensity of caspase-dependent and caspase-independent apoptosis reactions, which, together with the restoration of mitochondrial respiratory function, contributed to the decrease in the size of the necrosis zone of the brain.
Video Clip of Methodology:
Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: 8 min 7 sec Click to watch
Downloads
194
143 Read
41
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).
