Bufalin inhibits the growth and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of human gastric cancer cells via modulation of MEK/ERK pathway
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3329/bjp.v16i1.50548Keywords:
Bufalin, Gastric cancer, MEK/ERKAbstract
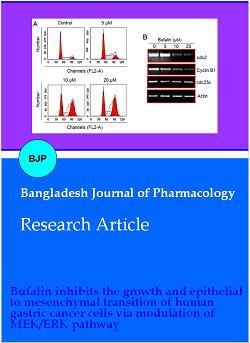
This study was designed to evaluate the anti-cancer effects of bufalin against the human gastric cancer cells and unveil the underlying mechanism. The results showed that bufalin inhibited the proliferation and colony formation of the MGC-803 gastric cancer cells and exhibited an IC50 of 10 μM. These antiproliferative effects were found to be due to the induction of G2/M cell cycle arrest. The G2/M cell cycle arrest was also concomitant with inhibition of cdc2, cdc25 and cyclin B1. Furthermore, bufalin suppressed the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, migration, and invasion of the MGC-803 gastric cancer cells. The Western blot analysis revealed that bufalin exerted its effects via deactivation of EK/ERK signaling pathway. Taken together, these results suggest the potential of bufalin as the lead molecule for the development of chemotherapy for gastric cancer.
Downloads
180
156
References
Dalton S. Cell cycle regulation of the human cdc2 gene. EMBO J. 1992; 11: 1797-804.
Hua W, Ten Dijke P, Kostidis S, Giera M, Hornsveld M. TGFβ-induced metabolic reprogramming during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020; 77: 2103-23.
Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Luan J, Duan H, Zhang F, Yagasaki K, Zhang G. Effects of bufalin on the proliferation of human lung cancer cells and its molecular mechanisms of action. Cytotechnology 2010; 62: 573-83.
Kallergi G, Papadaki MA, Politaki E, Mavroudis D, Georgoulias V, Agelaki S. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition markers expressed in circulating tumour cells of early and metastatic breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2011; 13: R59.
Lan YL, Lou JC, Jiang XW, Wang X, Xing JS, Li S, Zhang B. A research update on the anticancer effects of bufalin and its derivatives. Oncol Lett. 2019; 17: 3635-40.
Li D, Qu X, Hou K, Zhang Y, Dong Q, Teng Y, Zhang J, Liu Y. PI3K/Akt is involved in bufalin-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. Anti-cancer Drugs. 2019; 20: 59-64.
Li M, Yu X, Guo H, Sun L, Wang A, Liu Q, Wang X, Li J. Bufalin exerts antitumor effects by inducing cell cycle arrest and triggering apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 2014; 35: 2461-71.
Liu K, Zheng M, Lu R, Du J, Zhao Q, Li Z, Li Y, Zhang S. The role of CDC25C in cell cycle regulation and clinical cancer therapy: A systematic review. Cancer Cell Int. 2020; 20: 1-6.
Marampon F, Ciccarelli C, Zani BM. Biological rationale for targeting MEK/ERK pathways in anti-cancer therapy and to potentiate tumour responses to radiation. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20: 2530.
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Wong EW, Chang F, Lehmann B, Terrian DM, Milella M, Tafuri A, Stivala F. Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017; 1773: 1263-84.
Montagut C, Settleman J. Targeting the RAF–MEK–ERK pathway in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2009; 283: 125-34.
Nie Y, Wu K, Yu J, Liang Q, Cai X, Shang Y, Zhou J, Pan K, Sun L, Fang J, Yuan Y. A global burden of gastric cancer: The major impact of China. Exp Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017; 11: 651-61.
Prakash OM, Kumar A, Kumar P. Anticancer potential of plants and natural products. Am J Pharmacol Sci. 2013; 1: 104-15.
Qi HY, Qu XJ, Liu J, Hou KZ, Fan YB, Che XF, Liu YP. Bufalin induces protective autophagy by Cbl‐b regulating mTOR and ERK signaling pathways in gastric cancer cells. Cell Biol Int. 2019; 43: 33-43.
Qiu DZ, Zhang ZJ, Wu WZ, Yang YK. Bufalin, a component in Chansu, inhibits proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013; 13: 185.
Rawla P, Barsouk A. Epidemiology of gastric cancer: Global trends, risk factors and prevention. Prz Gastroenterol 2019; 14: 26.
Ribatti D, Tamma R, Annese T. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in cancer: A historical overview. Transl Oncol. 2020; 13: 100773.
Takai N, Kira N, Ishii T, Yoshida T, Nishida M, Nishida Y, Nasu K, Narahara H. Bufalin, a traditional oriental medicine, induces apoptosis in human cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012; 13: 399-402.
Thrift AP, El-Serag HB. Burden of gastric cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020; 18: 534-42.
Wang J, Cai H, Xia Y, Wang S, Xing L, Chen C, Zhang Y, Xu J, Yin P, Jiang Y, Zhao R. Bufalin inhibits gastric cancer invasion and metastasis by down-regulating Wnt/ASCL2 expression. Oncotarget 2018; 9: 23320.
Wang J, Cai H, Xia Y, Wang S, Xing L, Chen C, Zhang Y, Xu J, Yin P, Jiang Y, Zhao R. Bufalin inhibits gastric cancer invasion and metastasis by down-regulating Wnt/ASCL2 expre-ssion. Oncotarget 2018; 29: 23320.
Wang J, Xia Y, Zuo Q, Chen T. Molecular mechanisms underlying the antimetastatic activity of bufalin. Mol Clin Oncol. 2018; 8: 631-36.
Zhao H, Li Q, Pang J, Jin H, Li H, Yang X. Blocking autophagy enhances the pro-apoptotic effect of bufalin on human gastric cancer cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biol Open. 2017; 6: 1416-22.
Zhao H, Zhao D, Tan G, Liu Y, Zhuang L, Liu T. Bufalin promotes apoptosis of gastric cancer by down-regulation of miR-298 targeting bax. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015; 8: 3420.
Zheng L, He H, Shen X, Sun Y. Centipede Scolopendra suppesses cell growth in human epidermoid carcinoma cell A431. Bangladesh J Pharmacol. 2017; 12: 299-307.
Zheng Q, Jane JY, Li C, Li J, Wang J, Wang S. miR-224 targets BTRC and promotes cell migration and invasion in colorectal cancer. 3 Biotech. 2020; 10: 485.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).
