Seroprevalence and risk factors of hepatitis B virus surface antigen among the workers in a garment factory
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3329/bsmmuj.v10i4.34149Keywords:
Garment factory, Hepatitis B virus, Risk factor, Seroprevalence, Surface antigen, WorkerAbstract
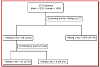
The purpose of this study is to find out the prevalence of seropositivity and risk factors associated with hepatitis B virus infection. A total of 2,737 readymade garment workers were initially screened after getting departmental as well as the individuals consent and simultaneously a questionnaire was filled up by the field research assistants to assess the risk factors. Initially 59 cases were found positive for hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg) by immunochromato-graphic test. Enzyme linked immunosorbant technique was then applied to the screened positive HBsAg individuals and four cases turned out as negative and therefore a total of 55 HBsAg positive cases were detected in this factory. Statistically significant risk factors associated with HBsAg positivity were jaundice, history of previous surgery and accident, needle stick injuries and unsafe injections. This study concludes that the seropositivity found garment workers is similar to the general population of Bangladesh.
Downloads
1036
127 Read
36
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2017 Mohammad Mizanur Rahman, Nasima Khatun, Ahsan Habib, Md. Rafiqul Islam, Farhana Islam

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.



